Ixl Student Login for Osceola Creek Middle School Updated FREE
Ixl Student Login for Osceola Creek Middle School
Yard–12,[a] from kindergarten to 12th grade, is an American expression that indicates the range of years of publicly supported master and secondary education found in the U.s., which is similar to publicly supported school grades before college in several other countries, such as Afghanistan, Australia, Canada, China, Ecuador, Arab republic of egypt, Republic of india, Iran, the Philippines, South korea, and Turkey.[1]
History [edit]
U.S. public didactics was conceived of in the belatedly 18th century. In 1790, Pennsylvania became the first country to require some form of free teaching for everyone regardless of whether they could afford it. New York passed similar legislation in 1805. In 1820, Massachusetts became the first land to create a tuition-complimentary high school, Boston English language.[two]
The first G–12 public school systems appeared in the early 19th century. In the 1830s and 1840s, Ohioans were taking a significant interest in the idea of public teaching. At that point in time, schools were commonly operated independently of each another, with little attempt at uniformity. The Akron School Police force of 1847 changed this. The urban center of Akron unified the operations, curriculum and funding of local schools into a single public schoolhouse district:
"Under the Akron School Law, there was to be i school commune encompassing the entire city. Inside that district would exist a number of unproblematic schools, with students divided into carve up "grades" based on achievement. When enough need existed, the school board would institute a high school also. Property taxes would pay for the new schoolhouse system. A school board, elected by the community, would make decisions well-nigh the organization'southward direction and rent the necessary professionals to run each schoolhouse. Illustrating the racism that existed in Ohio during this era, the Akron Schoolhouse Law excluded African-American children from the public school arrangement."[three]
In 1849, the country of Ohio enacted a law modeled after the Akron police which extended the idea of school districts to cover the remainder of the state.
By 1930, all 48 states had passed laws making education compulsory, and in 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Uncomplicated and Secondary Education Deed (ESEA), which committed the federal government to pregnant ongoing expenditures to each state for the purpose of sustaining local K–12 schoolhouse systems. The ESEA substantially fabricated K–12 education the law of the state.[iv]
Since its inception, public Chiliad–12 has been debated and bailiwick to several waves of reform throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. In the 1980s, Reagan'due south 'A Nation at Risk' initiative included provisions requiring public didactics to be evaluated based on standards, and teacher pay to be based on evaluations. In the 1990s, the Goals 2000 Deed and the "Improving America's Schools" act provided additional federal funding to states to bolster local M–12 systems. This was followed in the 2000s by a rigorous uptick in standards-based evaluations with the No Kid Left Behind Act, and the Race to the Top Human action. In 2015, President Barack Obama signed the Every Student Succeeds Human activity (ESSA), which returned some ability to state governments with respect to evaluations and standards.[5]
Etymology [edit]
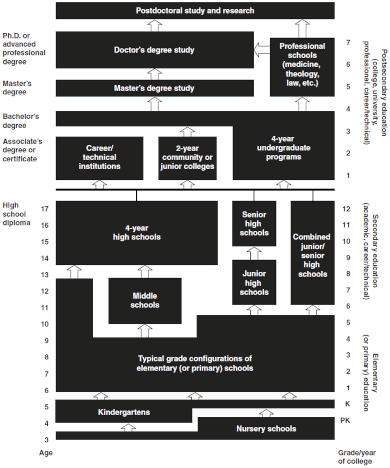
"The structure of teaching in the United States"
The expression "Chiliad–12" is a shortening of kindergarten (K) for 5–half dozen twelvemonth olds through 12th course (12) for 17–18 year-olds, as the outset and last grades, respectively, of gratis education[half dozen] in these countries. The related term "P–12" is likewise occasionally used in Australia and the Usa to refer to the sum of K–12 plus preschool instruction.[7] [8]
The image at the correct illustrates the instruction organization in the United States. The tabular array shows the progression of the education system starting with the basic Thou–12 organization then progressing through post-secondary educational activity. K–14 refers to M–12 plus two years of post-secondary where training was received from vocational-technical institutions or community or junior colleges. K-16 is 12 years of compulsory educational activity plus a 4-twelvemonth undergrad program. The K numbers refer to the years of educational attainment and continues to progress up appropriately depending on the degree being sought.[9]
Usage [edit]
The term is frequently used equally a kind of shorthand to collectively refer to the entirety of primary and secondary education, equally information technology is much easier than having to say i is referring in the amass to simple, middle, and high school education. Notwithstanding, information technology is rare for a schoolhouse district to actually teach all Yard–12 grades at one unified schoolhouse campus. Even the smallest schoolhouse districts try to maintain, at a minimum, a ii-tier stardom between an uncomplicated school (K–8) and a loftier schoolhouse (9–12).
The term is often used in school website URLs, generally appearing earlier the country code top-level domain (or in the U.s.a., the country top-level domain). The terms "PK–12", "PreK–12", or "Pre-K–12" are sometimes used to add pre-kindergarten.
It is as well used by American multinationals selling into the educational sector,[ten] such as Dell where U.k. customers are presented with this as a market segment pick.[11]
P–12 [edit]
In Commonwealth of australia, P–12 [12] is sometimes used in identify of M–12, peculiarly in Queensland, where information technology is used as an official term in the curriculum framework.[xiii] P–12 schools serve children for the thirteen years from prep until Year 12,[14] without including the separate kindergarten component. In Canada (Nova Scotia) P–12 is used commonly in place of Thousand–12 and serves students from grade Main through 12.
1000–14, K–16, K–18 and K–20 [edit]
K–fourteen educational activity also includes community colleges (the first two years of university). Thou–sixteen education[15] adds a four-year undergraduate academy degree. For simplicity purposes didactics shorthand was created to announce specific education levels of accomplishment. This shorthand is commonly used in manufactures, publications and educational legislation. The following list contains the most normally plant shorthand descriptors:
- P–xiv: Pre-schoolhouse to associate caste
- P–16: Pre-school to bachelor's degree
- P–eighteen: Pre-school to master's degree
- P–20: Pre-school to graduate caste
- G–14: Kindergarten to acquaintance caste
- M–16: Kindergarten to bachelor's degree
- K–eighteen: Kindergarten to main's caste
- K–20: Kindergarten to graduate degree
The Career Technical Education (CTE) Unit of the California Community Higher Economic Development and Workforce Preparation Division focuses on program coordination and advocacy, policy development and coordination with K–xviii workforce preparation and career and technical educational activity systems.[16]
The ASCCC Chancellor's Office Career Technical Education (CTE) Unit[17] of the Economic Development and Workforce Preparation Sectionalisation focuses on program coordination and advocacy, policy development and coordination with K–18 workforce training and career and technical education systems. Responsible for the implementation of the Vocational and Technical Education Human activity (VTEA), managing and coordinating activities that touch on other interagency and intra-agency objectives. In improver, the CTE Unit is besides responsible for the evolution, broadcasting, and implementation of the California Country Plan and the annual operation reports.[xviii]
Further reference to Thousand–18 education can exist found in this publication by Ann Diver-Stamnes and Linda Catelli[xix] in chapter 4 "College/University Partnership Projects for Instituting Modify and Comeback in K–18 Education".
See besides [edit]
- Day care
Notes [edit]
- ^ Spoken as "grand twelve", "k through twelve", or "grand to twelve".
References [edit]
- ^ Glavin, Chris (2014-02-06). "Educational activity in the U.s.a. | K12 Academics". www.k12academics.com . Retrieved 2018-07-23 .
- ^ Hornbeck, Dustin (2017-04-26). "Federal part in pedagogy has a long history | The Chat". world wide web.theconversation.com . Retrieved 2019-02-04 .
- ^ "Akron School Law | Ohio History Central". www.ohiohistorycentral.org/ . Retrieved 2019-02-04 .
- ^ Hornbeck, Dustin (2017-04-26). "Federal function in instruction has a long history | The Conversation". world wide web.theconversation.com . Retrieved 2019-02-04 .
- ^ Finn, Chester, Jr. (2013-03-xiv). "Short History of K-12 Reform | Hoover Institute". www.hoover.org . Retrieved 2019-02-04 .
- ^ "Online Didactics Programs & Schooling | K12". K12 . Retrieved 2018-07-23 .
- ^ Heritage College Cooranbong Archived 2011-07-23 at the Wayback Machine, NSW, Australia
- ^ "P–12 | US Department of Didactics". Retrieved 2016-09-16 .
- ^ "Assimilate of Education Statistics, 2012". nces.ed.gov . Retrieved 2018-02-05 .
- ^ "Peak 14 Companies in the Smart Education and eLearning Manufacture | Technavio". world wide web.technavio.com . Retrieved 2018-07-23 .
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-07-11. Retrieved 2011-07-04 .
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived re-create every bit title (link) - ^ Training, Department of Education and. "P-12 curriculum, cess and reporting framework". teaching.qld.gov.au. Archived from the original on 2014-08-04. Retrieved 2018-07-23 .
- ^ P–12 Curriculum Framework Archived 2014-08-04 at the Wayback Machine – pedagogy.qld.gov.au. Retrieved five December 2011.
- ^ "Why is P–12 career teaching important?". Department of Education and Grooming (Queensland). 2004. Archived from the original on 2009-12-xv. Retrieved 2010-01-01 .
- ^ "Why nosotros demand a Grand-16 education system - The Hechinger Written report". The Hechinger Report. 2010-05-11. Retrieved 2018-07-23 .
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-10-17. Retrieved 2012-08-27 .
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy every bit championship (link) http://www.desertcolleges.org/Faculty/Career.htm - ^ "CTE Community Collaborative : Career Technical Education (CTE)". world wide web.berkeleycitycollege.edu. Archived from the original on 2018-07-23. Retrieved 2018-07-23 .
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-09-08. Retrieved 2012-08-27 .
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived re-create as title (link) - ^ Barnes & Noble. "Commitment to Excellence: Transforming Education and Teacher Education in Inner-Urban center and Urban Settings". Barnes & Noble . Retrieved five February 2018.
Further reading [edit]
- Williams, Juliet A. (2013). "Girls can exist anything... but boys volition be boys: discourses of sex deviation in education reform debates". Nevada Police force Periodical. William S. Boyd School of Law. thirteen (2): 12.
Ixl Student Login for Osceola Creek Middle School
DOWNLOAD HERE
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K%E2%80%9312
Posted by: rubinhavenou.blogspot.com